44 ytm and coupon rate
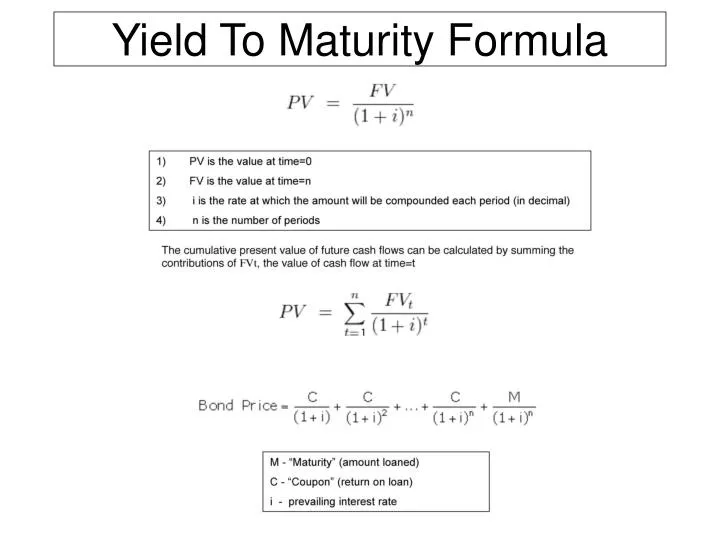
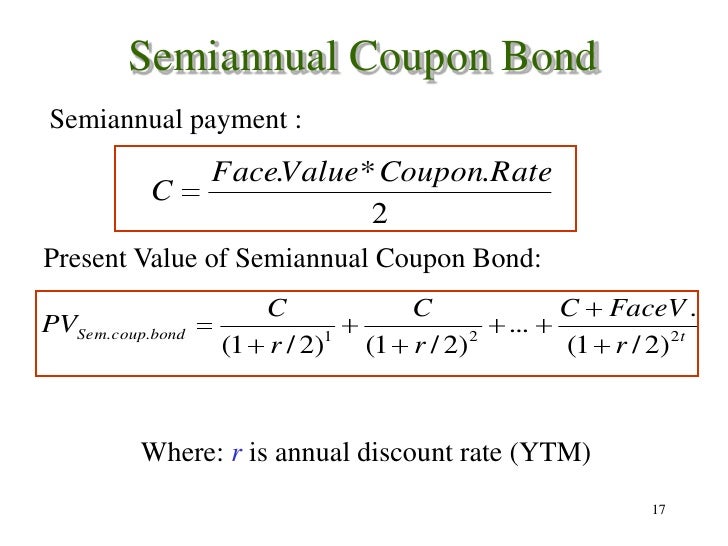
Yield to Maturity (YTM): Formula and Excel Calculator Semi-Annual Coupon Rate (%) = 6.0% ÷ 2 = 3.0%; Then, we must calculate the number of compounding periods by multiplying the number of years to maturity by the number of payments made per year. Number of Compounding Periods (n) = 10 × 2 = 20; As for our last input, we multiply the semi-annual coupon rate by the face value of the bond (FV) to arrive at the annual coupon of the bond. Yield to Maturity (YTM) Example Calculation Difference between YTM and Coupon Rates YTM accounts for both the interest payments made (the coupon rate) as well as any capital gains or losses. A coupon rate, on the other hand, is simply the interest rate that is paid out on a bond annually. It does not take into account any capital gains or losses. In order to calculate YTM, one must know the bond's face value, coupon rate, current market price, and time until maturity.
Coupon Rate Calculator | Bond Coupon As this is a semi-annual coupon bond, our annual coupon rate calculator uses coupon frequency of 2. And the annual coupon payment for Bond A is: $25 * 2 = $50. Calculate the coupon rate; The last step is to calculate the coupon rate. You can find it by dividing the annual coupon payment by the face value: coupon rate = annual coupon payment / face value

Ytm and coupon rate
Yield to maturity - Wikipedia It is the (theoretical) internal rate of return (IRR, overall interest rate): the discount rate at which the present value of all future cash flows from the bond (coupons and principal) is equal to the current price of the bond. The YTM is often given in terms of Annual Percentage Rate (A.P.R.), but more often market convention is followed. Difference Between YTM and Coupon rates 1. YTM is the rate of return estimated on a bond if it is held until the maturity date, while the coupon rate is the amount of interest paid per year, and is expressed as a percentage of the face value of the bond. 2. YTM includes the coupon rate in its calculation. Yield to Maturity vs. Coupon Rate: What's the Difference? To calculate the bond's coupon rate, divide the total annual interest payments by the face value. In this case, the total annual interest payment equals $10 x 2 = $20. The annual coupon rate for ...
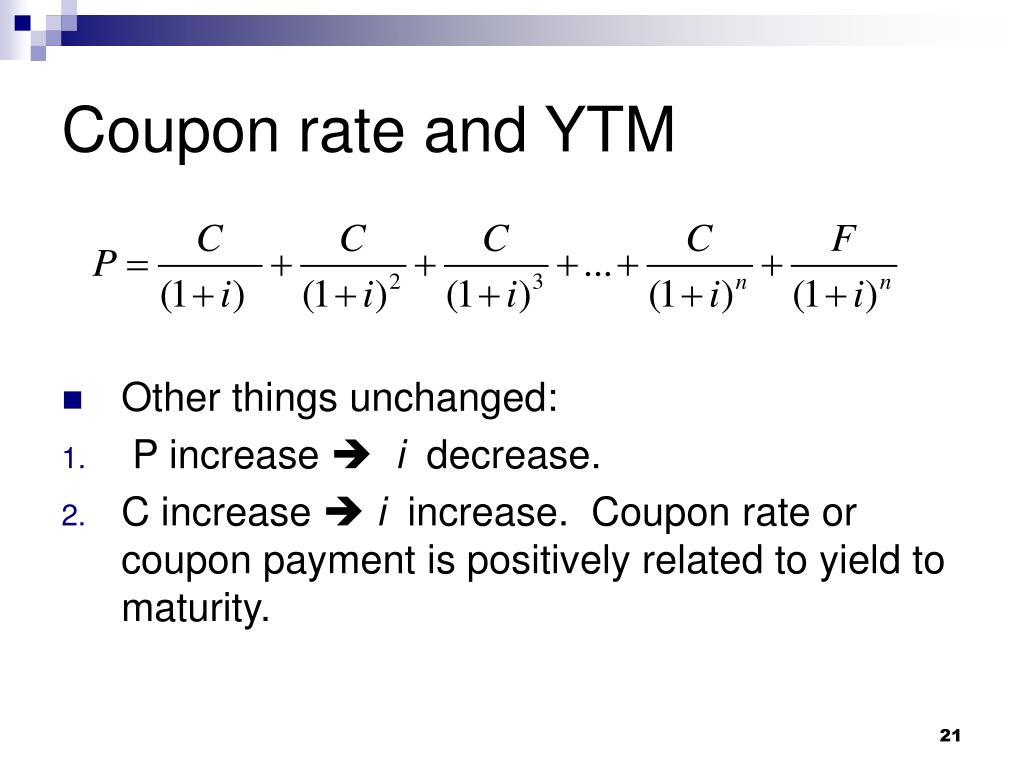
Ytm and coupon rate. Bond Pricing Formula | How to Calculate Bond Price? | Examples Since the coupon rate is higher than the YTM, the bond price is higher than the face value, and as such, the bond is said to be traded at a premium. Example #3. Let us take the example of a zero-coupon bond. Let us assume a company QPR Ltd has issued a zero-coupon bond with having a face value of $100,000 and maturing in 4 years. The prevailing ... Concept 82: Relationships among a Bond's Price, Coupon Rate, Maturity ... The relationship between a bond's price and its YTM is convex. Percentage price change is more when discount rate goes down than when it goes up by the same amount. Relationship with coupon rate. A bond is priced at a premium above par value when the coupon rate is greater than the market discount rate. Difference Between Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity Main Differences Between Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity. Coupon rate can be stated as the sum of money which a bond issuer has to pay relative to its bond value, while Yield to Maturity (YTM) can be defined as the total money which is to be accepted by an individual after the maturation. The coupon rate is also known as "Yield from the Bond." Calculating Cost of Debt: YTM and Debt-Rating Approach Given a tax rate of 35%, the after-tax cost of debt will be = 7.286% (1-35%) = 4.736%. Debt-Rating Approach. For certain types of debt, we may not have the market prices readily available, for example, bank loan. In such cases, the cost of debt can be based on company's rating by comparing it with the bonds with similar characteristics.
Yield to Maturity (YTM) - Overview, Formula, and Importance Yield to Maturity (YTM) - otherwise referred to as redemption or book yield - is the speculative rate of return or interest rate of a fixed-rate security, such as a bond. The YTM is based on the belief or understanding that an investor purchases the security at the current market price and holds it until the security has matured (reached its full value), and that all interest and coupon payments are made in a timely fashion. Difference Between Coupon Rate and Yield of Maturity Coupon Rate. Yield of Maturity. 1. The amount paid by the issuer to the bondholder until it's maturity is called coupon rate. The yield of maturity means the total return earned by the investor until it's maturity. 2. The rate of interest is paid annually at a coupon rate. Ytm And Coupon Rate rate ytm coupon and. hellman's mayo coupon april 2014. the palms oceanfront hotel coupon. aura glass art coupon code. coupon books for your boyfriend. gavin de becker the gift of fear free download. top 10 gifts for younger brother. toys r us christmas catalog coupons. long distance gifts for sister. anonymous gift exchange ideas. our gift to ... Yield to Maturity (YTM) Definition & Example | InvestingAnswers The bond will mature in 6 years and the coupon rate is 5%. To determine the YTM, we'll use the formula mentioned above: The estimated YTM for this bond is 13.220%. How Yield to Maturity Is Calculated (for Zero Coupon Bonds) Since zero coupon bonds don't have recurring interest payments, they don't have a coupon rate.
yield to maturity 和 coupon rate有什么区别_百度知道 1、yield to maturity:yield to maturity是到期收益率,又称最终收益率,是指在假设在投资收益率保持与YTM一样的情况下,所有的息票和本金收入向当期时刻折现,使得其现值正好等于目前的市场价格(初期需投资金额)的贴现率。. 2、coupon rate: coupon rate是票面利率,也是息票率,指印制在债券票面上的固定利率,通常是年利息收入与债券面额之比率,又称为名义收益率、票面 ... Yield to Maturity Calculator | Calculate YTM The YTM can be seen as the internal rate of return of the bond investment if the investor holds it until it matures and reinvests the coupon at the same interest rate. Hence, the YTM formula involves deducing the YTM r in the equation below: bond price = Σ k=1 n [cf / (1 + r) k], where: cf - Cash flows, i.e., coupons or the principal; r - YTM ... Important Differences Between Coupon and Yield to Maturity As such, yield to maturity can be a critical component of bond valuation. A single discount rate applies to all as-yet-unearned interest payments. It works the other way, too. Say prevailing rates fall from 2% to 1.5% over the first 10 years of the bond's life. Yield to Maturity (YTM) Definition - Investopedia Therefore, the current yield of the bond is (5% coupon x $100 par value) / $95.92 market price = 5.21%. To calculate YTM here, the cash flows must be determined first. Every six months (semi ...
Difference Between YTM and Coupon rates | Investing Post The YTM calculation takes into account: coupon rate, the price of the bond, time remaining until maturity, and the difference between the face value and the price. It is a rather complex calculation. The coupon rate, or, more simply stated, coupon of a particular bond, is the amount of interest paid every year.
Bond Yield to Maturity (YTM) Calculator - DQYDJ Annual Coupon Rate: 0%; Coupon Frequency: 0x a Year; Price = (Present Value / Face Value) ^ (1/n) - 1 = (1000 / 600) ^ (1 / 3) - 1= 1.6666... ^ (1/3) - 1 = 18.563%. Conclusion and Other Financial Basics Calculators. Use the Yield to Maturity as you would use other measures of valuation: a factor in your decision whether to buy or avoid a bond.
Yield to Maturity (YTM) - Meaning, Formula and Examples Here YTM will be higher than the coupon rate, which is 8%. If the bond is selling for a higher price than the face value, this means the interest rate in the market is lower than the coupon rate. This indicates that the YTM is lesser than the coupon rate.
Yield to Maturity vs. Coupon Rate: What's the Difference? To calculate the bond's coupon rate, divide the total annual interest payments by the face value. In this case, the total annual interest payment equals $10 x 2 = $20. The annual coupon rate for ...
Difference Between YTM and Coupon rates 1. YTM is the rate of return estimated on a bond if it is held until the maturity date, while the coupon rate is the amount of interest paid per year, and is expressed as a percentage of the face value of the bond. 2. YTM includes the coupon rate in its calculation.
Yield to maturity - Wikipedia It is the (theoretical) internal rate of return (IRR, overall interest rate): the discount rate at which the present value of all future cash flows from the bond (coupons and principal) is equal to the current price of the bond. The YTM is often given in terms of Annual Percentage Rate (A.P.R.), but more often market convention is followed.




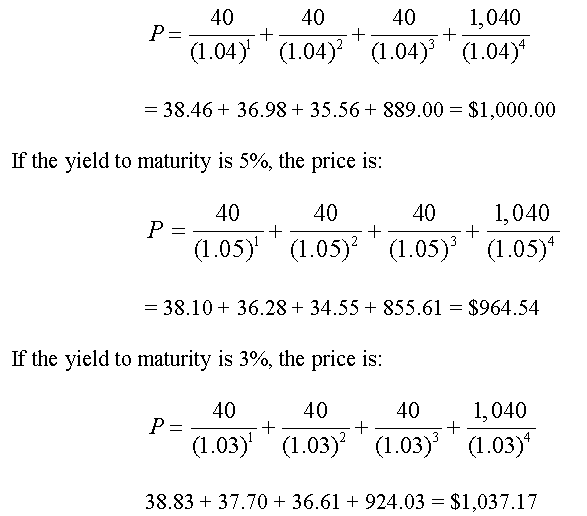

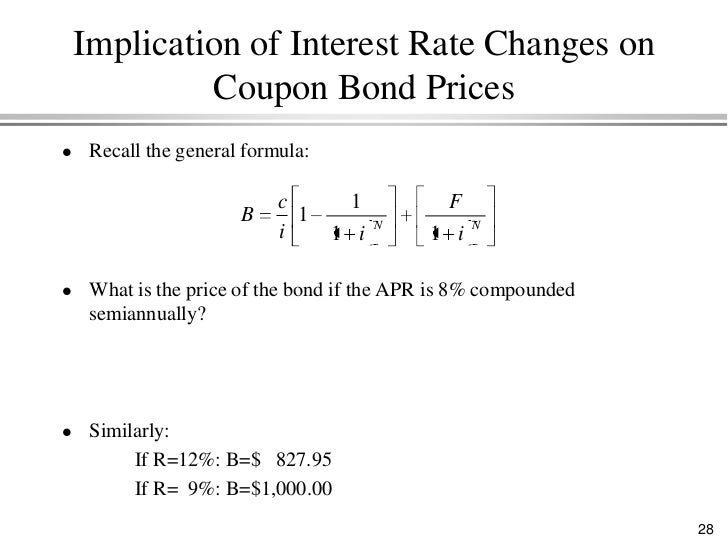


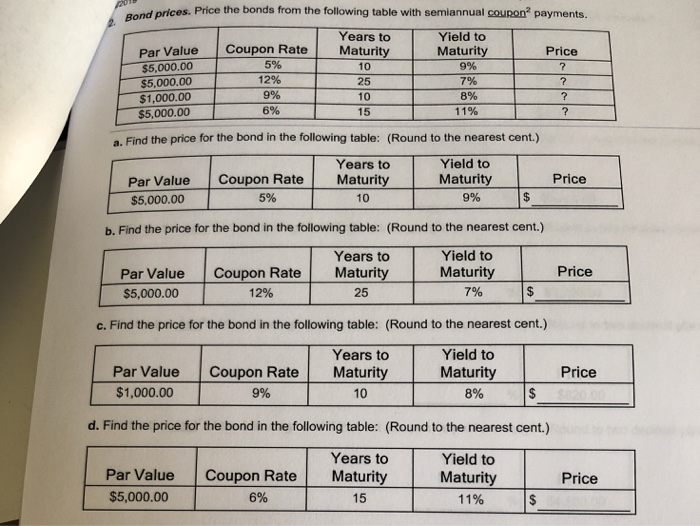

Post a Comment for "44 ytm and coupon rate"